The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is America’s civil space program. It is a global leader in space exploration. The organization is having 18,000 diverse workforces. There is other U.S. academia, contractors, international and commercial partners working with NASA, who want to discover, explore, and expand the knowledge of space for humanity.
Across the country, there are 20 centers and facilities. National Laboratory in space, NASA, studies our planet Earth and its climate, Sun, Solar System and galaxies beyond our solar system. Also, NASA is leading a Moon to Mars exploration approach. They are working with U.S. industry, academia, and international partners to develop the technology and to send the science research on Moon and Mars.
All You Should Know About NASA
Creation
The National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) in 1946 began working on the rocket planes such as the supersonic Bell X-1. There was a challenge to launch an artificial satellite in the early 1950s. It was for International Geophysical Year (1957-58). On October 4, 1957, Soviet Space Program launched the world’s first artificial satellite Sputnik 1. The attention of the United States turned towards their fledgling space efforts.
Sputnik 1 was considered a threat to national security and technological leadership. As a result, on January 12, 1958, NACA organized Special Committee on Space Technology. It was headed by Guyford Stever. Later on, Eisenhower signed the National Aeronautics and Space Act, establishing NASA on July 29, 1958. Operations of NASA began on October 1, 1958. It had 8,000 employees with an annual budget of $100 million.
In the beginning, NASA had three research laboratories; Ames Aeronautical Laboratory, Langley Aeronautical Laboratory, and Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. Also, there were two small facilities at that time.
Symbols of NASA
From the space shuttle wing to the top of the NASA homepage, the official badge of the agency is the best-known symbol around the globe.
The red, white, and blue round badge that is nicknamed a meatball was designed by employee James Modarelli in 1959. It was NASA’s second year. The design is having different aspects of the mission of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. The round shape of insignia represents the planet and stars represent space. The red V-shaped wing is the representation of aeronautics and the circular orbit around the name of the agency presents space travel.
The meatball insignia of NASA was a common symbol for 16 years. In 1975, it was decided to create a modern logo for the agency. It was required to have a unique typestyle for the logo. Hence, it was named as worm logo. The worm logo was used from 1975 to 1992. At the time of retirement of the worm logo, the classic meatball insignia returned for official use.
Projects Leading to Space Exploration
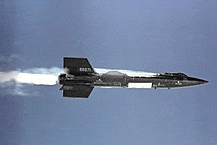
X-15 Program (1954 – 1968)
NASA inherited NACA’s X-15 experimental rocket-powered hypersonic research aircraft. Three planes were built in 1955. To fly these hypersonic research aircraft, 12 pilots were selected from the Air Force, NACA, and Navy. The X-15 aircraft made a total of 1199 flights during the period of ten years from 1959 to 1968. It set unofficial world records for speed and altitude of 4,520 mph (Mach 6.7) and 354,200 feet.
The information gained from X-15, a highly successful program contributed to the development of Mercury, Apollo, and Gemini spacecraft and Space Shuttle Programs.
Project Mercury (1958-1963)
US Air Force’s Man in Space Soonest program was adopted by NASA. It was considered that spacecraft were designed like X-15 and small ballistic space capsules. In 1958, space plane concepts were rejected and ballistic capsules were favored. It was renamed by NASA as Project Mercury. The first seven astronauts were selected from Air Force, Navy, and Marine from test pilot programs.
Alan Shepard was the first American in space abroad a capsule named Freedom 7 on May 5, 1961. John Glenn was the first American who was launched into orbit on Atlas’s launch vehicle on February 20, 1962. Glenn completed the 3 orbits around the Earth. Later on, Soviet Union (USSR) launched a single-pilot Vostok spacecraft as a competition to Project Mercury.
Project Gemini (1961-1966)
Based on Project Mercury, it was to grow the spacecraft capabilities that could go for long-duration flights. In 1961, Project Gemini was started as a two-man program that was to compete with the soviet’s lead. Gemini 3, the first crewed Gemini flight was flown on March 23, 1965, by Gus Grissom and John Young.
Nine missions were followed in 1965 and 1966 to demonstrate the endurance of the mission of fourteen days, docking, rendezvous, and practical Extravehicular activity (EVA). It was done to collect medical data such as the effect of weightlessness on humans.
Project Apollo (1960-1972)
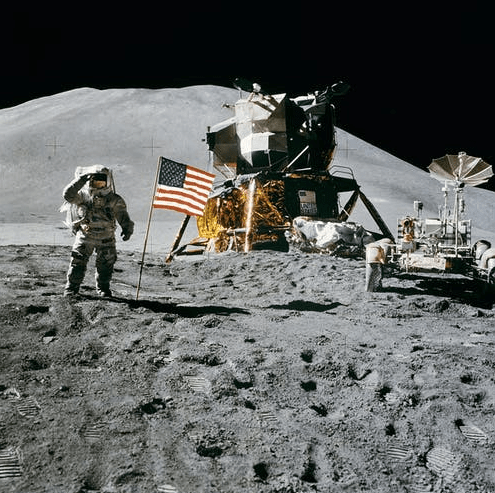
Apollo was the most expensive American scientific program. It cost around $20 billion in 1960s dollars that makes $225 billion in present-day US dollars. The spacecraft was bigger than previous projects and had two main parts. The Apollo Lunar Module (LM) and combined Command and Service Module (CSM). LM was supposed to be left on the Moon and Command Module would return to the Earth having three astronauts in it.
Apollo 11 mission in July 1969 was for the moon landing. The first person to walk on the Moon was Neil Armstrong. Armstrong was followed by Buzz Aldrin after 19 minutes and the third astronaut Michael Collins orbited above. These missions helped to collect the scientific data from 381.7 kilograms of lunar samples.
The topics covered from the experiments included meteoroids, soil mechanics, seismology, lunar ranging, heat flow, solar wind, and magnetic fields. Landing on the Moon ended the space race. Project Apollo set major milestones to research other planets and galaxies.
Journey to Mars (2010-2017)
President Obama planned to develop a U.S. private spaceflight capability to transport astronauts to the International Space Station by replacing Russian Soyuz capsules. For ISS emergency evacuation from the United States, Orion capsules were used. On April 15, 2010, during a speech at Kennedy Space Center, Obama proposed a new heavy-lift vehicle (HLV) that replace the Ares V.
A manned mission orbiting Mars in the mid-2030s was proposed by Obama. The NASA authorization license was passed by Congress and enacted on October 11, 2010. This law officially ended the Constellation program.
Other Interesting Facts About NASA
- The goal of sending a man to the moon by the end of the 1960s was given by President John F. Kennedy. As a result, the first men walked on the moon on July 20, 1969, as a part of the Apollo 11 mission.
- 12 men have walked on the moon during the Apollo missions.
- Apollo 13 lunar landing was aborted in 1970 because of an oxygen tank explosion.
- The space shuttle named Enterprise was the first shuttle for the reusable spacecraft fleet. It was created for testing. Hence, it never flew in space.
- Enterprise was initially named as Constitution. The fans of the TV show Star Trek ran a successful campaign to change the name.
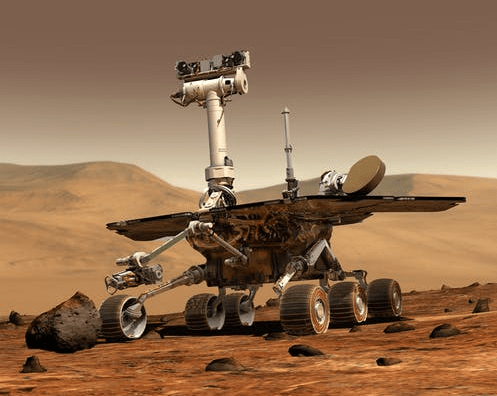
- In 1997, the first rover landed on Mars. The four rovers were named Sojourner, Spirit, Opportunity, and Curiosity. The fifth rover is known as Perseverance that landed on Mars for scientific studies.
- Perseverance is the heaviest of all rovers landed on Mars. It weighs 2,260 pounds. It is as heavy as a hippo.
- Astronauts who spend 6 months on the International Space Station can grow up to 3 percent taller.
- Apart from the major mission, NASA shares information with its partners to make life better for people on Earth.
- NASA supports educational efforts in STEM to increase the diversity in their future workforce.
Goals of NASA
The goal of NASA is to extend and sustain human activities across the solar system. They are working to expand the scientific understanding of Earth and the Universe. Also, they are creating innovative space technologies to studies the neighboring galaxies. Hence, they are working on advanced aeronautics research.
NASA – A Civilian Space Program
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration an American civil program working on the research and study of Earth, Solar System, and Galaxies neighboring our Milky Way. In all these years, the agency has been looking for life possibilities on other planets. Finding life possibilities on other planets can be tentative and exploratory steps towards advanced space research. Also, NASA is funding the educational department to increase the workforce and participants in space research in the future.